打開文件檔,存成java的形式↓
然後把class Person1剪下,存成另一個檔案↓
修改一下
在Object1加入
Person1 p3 = new Person1();
p3.checkWeight();
在Person1中加入
Person1()
{ name = "宜靜";
weight = 42; }
這樣子程式碼找不到條件時就會在
Person1() 中找
結果↓
接著去老師的Blogger複製程式碼
// with event
//Swing, JButton類別 有ActionListener
//Swing, JButton類別
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class SwingEightPuzzleEvent extends JFrame implements ActionListener
{
//static JFrame myfrm=new JFrame("JButton class"); // Java Class JFrame
//static AwtTestEvent myfrm=new AwtTestEvent("JFrame 1 "); // Java Class JFrame
static JTextField tbx1=new JTextField(2); // 建立1文字方塊物件
static JButton buttons[]=new JButton[10];
static JLabel labels[]=new JLabel [10];
public SwingEightPuzzleEvent()
{}//建構子
public static void main(String args[])
{
SwingEightPuzzleEvent myfrm=new SwingEightPuzzleEvent();
String numbers[] = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8"};
FlowLayout flow=new FlowLayout();
GridLayout grid12= new GridLayout(1,2);
GridLayout grid33= new GridLayout(3,3);
myfrm.setLayout(grid12);
myfrm.setSize(450,450);
JPanel p1 = new JPanel(grid33); //實作 panel 1
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++)
{
buttons[i] = new JButton(numbers[i]); // create buttons
p1.add(buttons[i], grid33); // 在 panel 1內加入按鈕陣列
}
myfrm.add(p1); // 在視窗myfrm 內加入 panel 1
JPanel p3 = new JPanel(grid33); //實作 panel 3
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++)
{
labels[i] = new JLabel(); // create labels
p3.add(labels[i], grid33); // 在 panel 1內加入按鈕陣列
}
myfrm.add(p3); // 在視窗myfrm 內加入 panel 3
JPanel p2 = new JPanel(flow); //實作 panel 2
JButton btn1=new JButton("JButton 1"); // 建立按鈕物件 btn1
btn1.addActionListener(myfrm);
p2.add(tbx1); // 在 panel 2內加入文字方塊
p2.add(btn1); // 在 panel 2內加入按鈕
myfrm.add(p2); // 在視窗myfrm 內加入 panel 2
myfrm.setVisible(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
String numbers[] = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8"};
//int rndno;
//String stringValue;
//stringValue=tbx1.getText();
//int intValue = Integer.parseInt(stringValue);
//System.out.println(intValue);
//labels[intValue].setText(stringValue);
/*
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++)
{
//rndno=(int) (Math.random()*9);
//System.out.println(rndno);
//numbers[i]=String.valueOf(rndno);
//buttons[i].setLabel(numbers[i]);
}
*/
//tbx1.setText(numbers[0]);
//buttons[rndno].setBackground(Color.blue);
//labels[rndno].setText(numbers[0]);
}
}
開始幫他瘦身囉~
把一些可以移到建構子的程式移進去建構子
public SwingEightPuzzleEvent()
{}//建構子
{}//建構子
如果建構子跟class main 都會用到的程式就移到最上面去
這樣就可以兩個都包含在內了
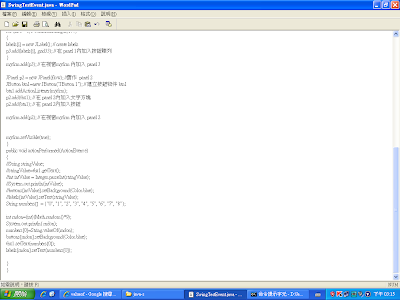
整理過後的程式↓
// with event
//Swing, JButton類別 有ActionListener
//Swing, JButton類別
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class SwingEightPuzzleEvent extends JFrame implements ActionListener
{
//static JFrame myfrm=new JFrame("JButton class"); // Java Class JFrame
//static AwtTestEvent myfrm=new AwtTestEvent("JFrame 1 "); // Java Class JFrame
static JTextField tbx1=new JTextField(2); // 建立1文字方塊物件
static JButton buttons[]=new JButton[10];
static JLabel labels[]=new JLabel [10];
static FlowLayout flow=new FlowLayout();
static GridLayout grid33= new GridLayout(3,3);
static JButton btn1=new JButton("JButton 1"); // 建立按鈕物件 btn1
static JPanel p1 = new JPanel(grid33); //實作 panel 1
static JPanel p2 = new JPanel(flow); //實作 panel 2
static JPanel p3 = new JPanel(grid33); //實作 panel 3
static String numbers[] = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8"};
static GridLayout grid12= new GridLayout(1,2);
public SwingEightPuzzleEvent()
{
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++)
{
labels[i] = new JLabel(); // create labels
p3.add(labels[i], grid33); // 在 panel 1內加入按鈕陣列
}
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++)
{
buttons[i] = new JButton(numbers[i]); // create buttons
p1.add(buttons[i], grid33); // 在 panel 1內加入按鈕陣列
}
p2.add(tbx1); // 在 panel 2內加入文字方塊
p2.add(btn1); // 在 panel 2內加入按鈕
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
SwingEightPuzzleEvent myfrm=new SwingEightPuzzleEvent();
myfrm.setLayout(grid12);
myfrm.setSize(450,450);
myfrm.add(p1); // 在視窗myfrm 內加入 panel 1
myfrm.add(p3); // 在視窗myfrm 內加入 panel 3
btn1.addActionListener(myfrm);
myfrm.add(p2); // 在視窗myfrm 內加入 panel 2
myfrm.setVisible(true);
}
今天的作業就是去http://www.rgagnon.com/javadetails/java-0144.html複製程式碼
分別執行套件的運用
就完成囉~